Activity,Window,View的关联与理解
Activity,Window,View相关
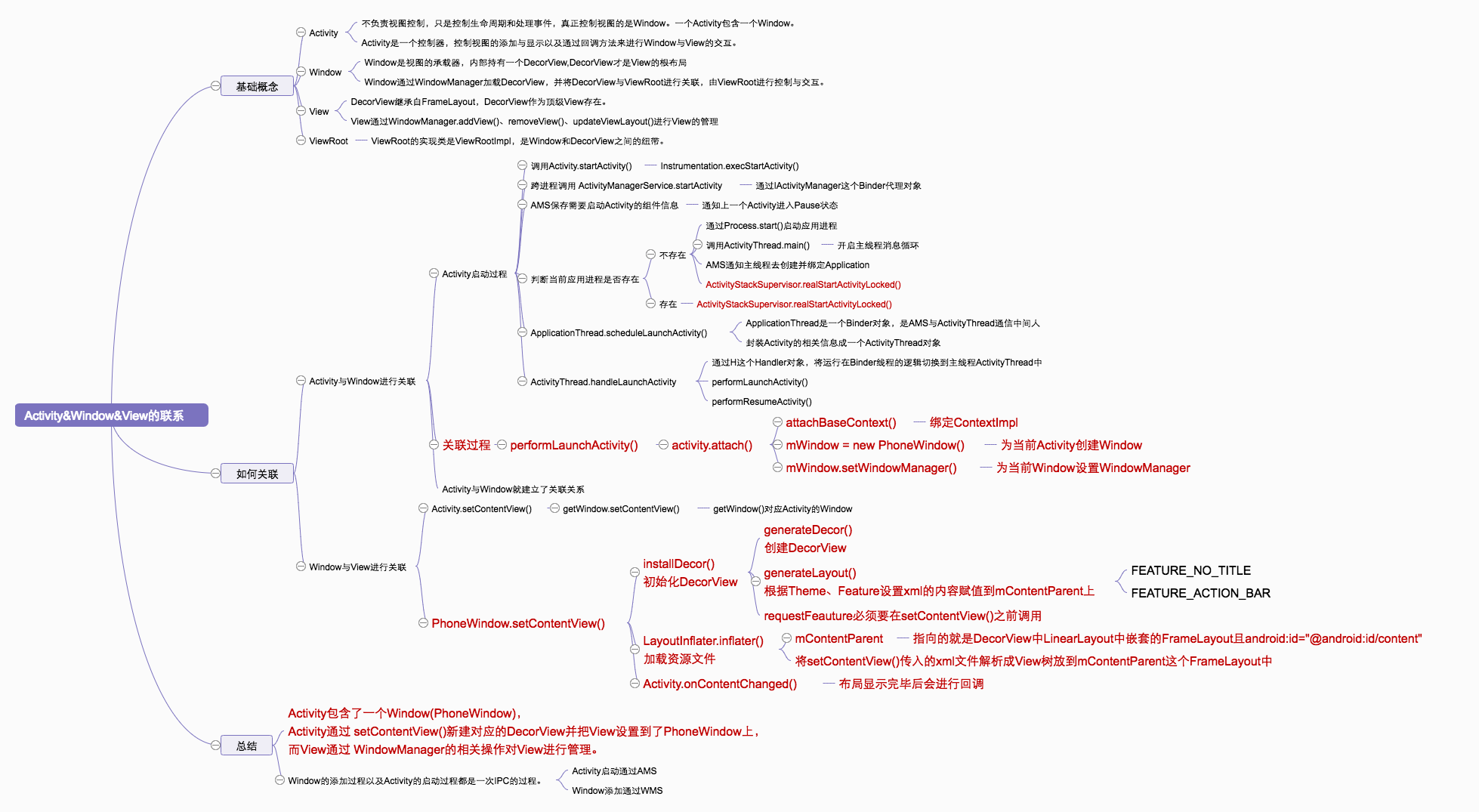
1. 什么是Activity,Window,View以及职能简介
- Activity:主要负责生命周期与事件分发入口,不直接管理底层绘制。一个Activity通常对应一个
PhoneWindow。Activity更像控制器,通过回调与Window/View协作。 - Window:Window是视图承载器,抽象类,Activity中的实现通常是
PhoneWindow。它持有DecorView,并负责把页面内容组织到窗口结构中。 - View:
DecorView继承自FrameLayout,作为顶级View容器,内部一般包含标题栏区域与内容栏(android.R.id.content)。Activity通过setContentView()把业务布局放入内容栏。 - ViewRoot:实现类是
ViewRootImpl,是WindowManagerService与DecorView在应用进程侧的桥接点。ViewRootImpl不属于View树节点,但实现了ViewParent并驱动measure/layout/draw。
2. Activity如何和Window,View关联(附源码)
Activity和Window关联
Activity启动过程在此简述下Activity的启动过程:
- 调用
ContextImpl.startActivity()实质调用ContextImpl.startActivityForResult() - 执行到
performLaunchActivity()在其中完成启动流程 - 通过
Instrumentation.newActivity使用类加载器创建Activity对象 - 通过
LoadedApk.makeApplication()尝试创建Application对象(Application已被创建则跳过) - 创建
ContextImpl对象,并执行Activity.attach()完成一些重要数据的初始化 - 最终调用
Activity.onCreate()完成启动流程。
其中Activity和Window的关联发生在Activity.attach()中
1 | |
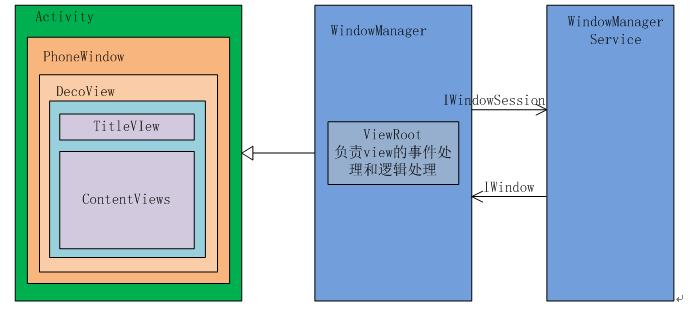
其中PhoneWindow就是Activity的根Window,可以在其上添加其他的Window(例如Dialog),PhoneWindow就是Activity与View之间的桥梁,Activity无法直接操作View。
Window和View关联
Activity无法直接和View交互,需要通过Window管理
1 | |
Activity通过setContentView()加载要显示的布局,观察源码可知还是通过Window进行了加载操作。
这里要区分两件事:
setContentView()完成的是“把布局inflate进DecorView的内容区”;真正显示到屏幕还需要后续addView -> setView -> performTraversals链路。
加载View
1 | |
Activity通过setContentView()调用到PhoneWindow.setContentView()执行DecorView的创建流程。
DecorView直接和PhoneWindow进行关联,其内部包含了我们定义的布局(ContentView)以及一个titlebar。
显示View
上述方法只是创建了一个DecorView,而没有完成真正的显示流程。接下来需要结合Activity生命周期与窗口添加流程来看“何时可见”。
更完整的显示链路如下:
ActivityThread.handleResumeActivity() -> WindowManagerImpl.addView() -> WindowManagerGlobal.addView() -> ViewRootImpl.setView() -> requestLayout() -> performTraversals() -> draw()
这条链路里,setContentView()负责“装内容”,addView/setView负责“挂到窗口并进入绘制调度”。
生命周期与首帧关系
onCreate():完成页面初始化与视图装载。onResume():进入可交互生命周期,但不等于首帧已提交到屏幕。onWindowFocusChanged(true):常用于感知页面真正进入前台焦点状态。
因此,“可见”是一个从生命周期到渲染提交的过程,不是单点事件。
输入事件如何进入View树
窗口建立后,输入事件大致走这条路径:
InputDispatcher -> InputChannel -> ViewRootImpl -> DecorView -> ViewGroup -> View
这也是为什么ViewRootImpl既出现在绘制链路,也出现在输入分发链路中。
View需要通过Window才能展示在Activity上。
关系速查表
| 对象 | 主要职责 | 是否在View树中 | 典型关键方法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Activity | 生命周期与交互入口 | 否 | attach()、setContentView() |
| PhoneWindow | 窗口容器与页面框架 | 否 | setContentView()、installDecor() |
| DecorView | 页面顶层View容器 | 是 | dispatchTouchEvent()、draw() |
| ViewRootImpl | 驱动绘制与输入桥接 | 否 | setView()、performTraversals() |
| WMS | 系统侧窗口管理 | 否(系统进程) | addWindow()、relayoutWindow() |
3.总结
Activity负责生命周期与事件入口,Window负责承载与组织页面结构,DecorView是顶层View容器。
setContentView()主要完成布局装载;真正显示依赖WindowManagerGlobal.addView() -> ViewRootImpl.setView() -> performTraversals()。ViewRootImpl是应用进程侧的关键桥接层,既串起绘制流程,也串起输入分发流程。
Activity包含一个PhoneWindow,Activity通过setContentView()把布局放入PhoneWindow的内容区域;随后由WindowManager体系执行addView()/updateViewLayout()/removeView()完成窗口层管理。
从跨进程角度看:Activity启动主链路依赖AMS,窗口添加与更新主链路依赖WMS(经IWindowSession进行通信)。