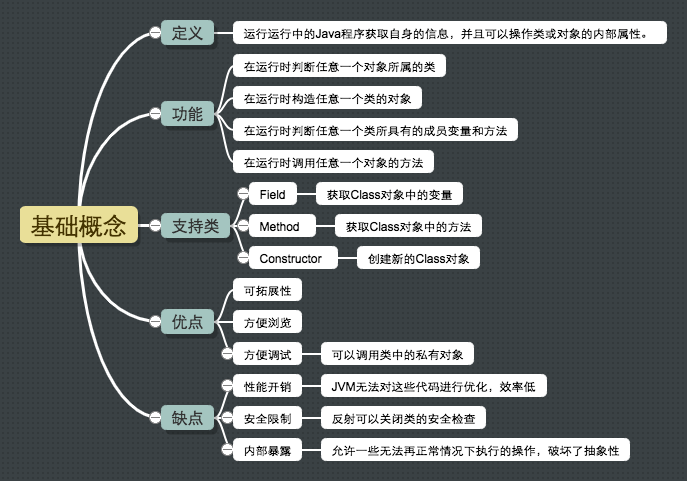
Java反射机制基础 反射机制定义 反射(Reflection)是Java的特征之一,它允许运行中的Java程序获取自身的信息,并且可以操作类或对象的内部属性。对于任何一个类,能够知道这个类中的所有属性和方法;对于任何一个对象,都能够调用它的任意一个方法和属性。
反射机制功能 通过反射,可以在运行时获取程序中的每一个类型的成员和成员信息。利用Java的反射机制可以动态的创建对象并调用其属性。反射可以提供运行时的类信息,并且可以支持这个类在运行过程中加载进来,甚至在编译时也没有加入编译的类。
主要提供了如下功能:
在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法
生成动态代理
一切都是在运行时而不是编译时。
反射机制支持 由java.lang.reflect提供反射机制的支持,主要包含了三个类:
Field:使用getField()和setField()读取和修改Field对象关联的字段Method:使用invoke()调用Method对象关联的方法Constructor:创建新的对象
反射机制优点
可拓展性 :应用程序可以利用全限定名创建可扩展对象的实例,来使用来自外部的用户自定义类类浏览器和可视化开发环境 :可以枚举类的成员调试器和调试工具 :可以调用类中的private或者protected的对象。
反射机制缺点
性能开销 :反射涉及了动态类型的解析,所以JVM无法对这些代码进行优化。导致效率低安全限制 :使用反射要求在没有安全限制的环境下去进行内部暴露 :由于反射允许代码执行一些正常情况下无法执行的操作(访问私有变量或方法 ),反射代码也破坏了抽象性,当内部代码发生改变时,反射的代码也需要进行相应调整。
Java反射机制使用场景
用于逆向代码,反编译
与注解相结合的框架 例如Retrofit使用的运行时注解
单纯的利用反射机制的框架 例如EventBus所以那些Event都不能被混淆
动态代理
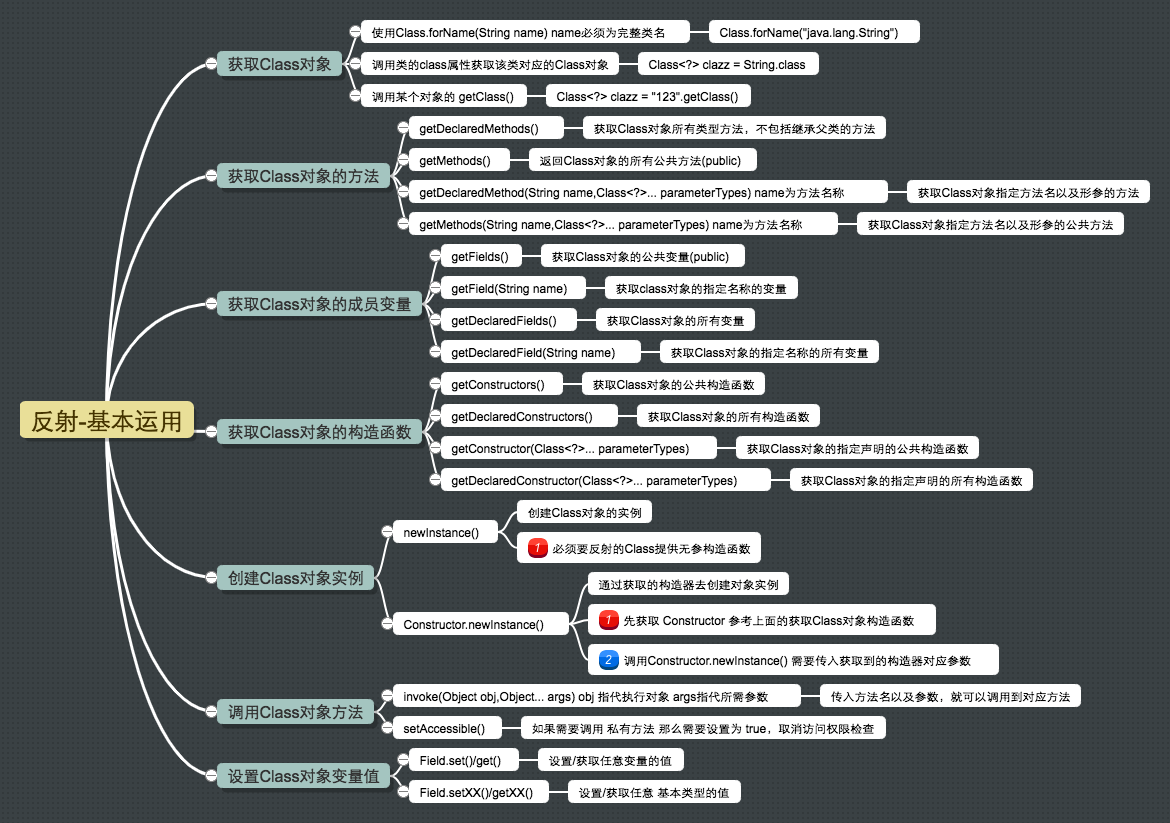
Java反射机制的基本运用 获得Class对象
每个类被加载后,系统都会为其生成一个对应的Class对象,通过该Class对象就可以访问到JVM中的这个类
获取Class对象的方法有如下三种
使用Class.forName(String className/*必须完整包名*/)获取对象。 1 Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.example.wxy.FieldUtil" );
调用类的class属性来获取该类对应的Class对象 1 Class<?> clazz = FieldUtil.class;
调用某个对象的getClass(), 1 2 Person person = new Person ();
获取Class对象的方法 主要有以下几个方法:
getDeclaredMethods()
返回类或接口声明的所有方法,包括public(公共)、private(私有)、protected(保护),default(默认),但不包括继承的方法
1 public Method[] getDeclaredMethods() throws SecurityException
getMethods()
返回类或接口所有的公共(public)方法,包括父类的公共(public)方法
1 public Method[] getMethods() throws SecurityException
getDeclaredMethod()
返回Class对象对应类的且带指定形参列表的所有方法
1 2 3 4 5 public Method getDeclaredMethod (String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
getMethod()
返回Class对象对应类的且带指定形参列表的公共(public)方法
1 2 3 4 5 private Method getMethod (String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
实例分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 public class reflect {public static void main (String[] args) {try {Method addMethod = methodClass.getDeclaredMethod("add" , int .class, int .class);Method subMethod = methodClass.getMethod("sub" , int .class, int .class);"Declared Method " +addMethod);"public Method " +subMethod);for (Method method : methods) {"Public Methods " +method);for (Method method : declaredMethods) {"Declared Methods " +method);catch (Exception e) {class MethodClass {public final int a = 4 ;private int add (int a, int b) {return a + b;public int sub (int a, int b) {return a - b;private int MethodClass.add(int ,int )public int MethodClass.sub(int ,int )public int MethodClass.sub(int ,int )public final void java.lang.Object.wait(long ,int ) throws java.lang.InterruptedExceptionpublic final native void java.lang.Object.wait(long ) throws java.lang.InterruptedExceptionpublic final void java.lang.Object.wait() throws java.lang.InterruptedExceptionpublic boolean java.lang.Object.equals(java.lang.Object)public java.lang.String java.lang.Object.toString()public native int java.lang.Object.hashCode()public final native java.lang.Class java.lang.Object.getClass()public final native void java.lang.Object.notify()public final native void java.lang.Object.notifyAll()private int MethodClass.add(int ,int )public int MethodClass.sub(int ,int )
获取Class对象的成员变量 主要有以下方法:
getFields()
获取Class对象的public属性的所有变量
1 public Field[] getFields() throws SecurityException
getField()
获取Class对象的指定public属性变量
1 public Field getField (String name) throws NoSuchFieldException {
getDeclardFields()
获取Class对象的所有变量
1 public native Field[] getDeclaredFields();
getDeclardField()
获取Class对象的指定属性变量
1 public native Field getDeclaredField (String name) throws NoSuchFieldException
实例分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 public class reflect {public static void main (String[] args) {try {Field field = methodClass.getField("a" );Field declaredField = methodClass.getDeclaredField("c" );for (Field f : fields) {"Public Fields " + f);for (Field f : declaredFields) {"Declared Fields " + f);catch (Exception e) {class MethodClass {public final int a = 4 ;private final int c = 5 ;public final int MethodClass.apublic final int MethodClass.aprivate final int MethodClass.c
获取Class对象的构造函数 getConstructors()
获取Class对象的Public构造函数
1 public Constructor<?>[] getConstructors() throws SecurityException
getDeclaredConstructors()
获取Class对象的所有构造函数
1 public Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors() throws SecurityException
getConstructor()
获取指定声明的public构造函数
1 2 3 4 public Constructor<T> getConstructor (Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException
getDeclaredConstructor()
获取指定声明的构造函数
1 2 3 4 public Constructor<T> getDeclaredConstructor (Class<?>... parameterTypes) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException
实例分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class reflect {public static void main (String[] args) {try {int .class,int .class);int .class,int .class,int .class);for (Constructor f : constructors) {"Public Constructors " + f);for (Constructor f : declaredConstructors) {"Declared Constructors " + f);catch (Exception e) {class MethodClass {public MethodClass (int a ,int b) {private MethodClass (int a,int b,int c) {public MethodClass (int ,int ) public MethodClass (int ,int ) private MethodClass (int ,int ,int )
创建Class对象实例 newInstance()
创建对象的实例 需要对应Class有无参构造函数
1 public native T newInstance () throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException;
Constructor.newInstance()
通过构造器去创建对象实例
1 public T newInstance (Object ... initargs) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
实例分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class reflect {public static void main (String[] args) {try {Object object = methodClass.newInstance();int .class,int .class);Object object1 = constructor.newInstance(1 ,2 );"newInstance() " +object.getClass());"Constructor.newInstance() " +object1.getClass());catch (Exception e) {class MethodClass {public int a = 4 ;private int b = 6 ;private int c = 5 ;public MethodClass () {public MethodClass (int a, int b) {this (a, b, 0 );private MethodClass (int a, int b, int c) {this .a = a;this .b = b;this .c = c;class MethodClass class MethodClass
调用Class对象方法 invoke()
传入方法名和参数,就可以调用到对应方法
1 2 3 4 @CallerSensitive @FastNative public native Object invoke (Object obj, Object... args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException;
@FastNative:Android 8.0新增加的注解,可以更快速的进行原生调用
@CallserSensitive:跳过检查直接确定调用的对象
实例分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class reflect {public static void main (String[] args) {try {Object object = methodClass.newInstance();Method addMethod = methodClass.getDeclaredMethod("add" , int .class, int .class);true );1 ,2 );Method subMethod = methodClass.getMethod("sub" , int .class, int .class);2 ,1 );catch (Exception e) {class MethodClass {public MethodClass () {private int add (int a, int b) {"I`m reflect private method " + a+b);return a + b;public int sub (int a,int b) {"I`m reflect public method" + a-b);return a - b;private method 3 public method 1
当通过Method.invoke()调用对应方法时,要求程序必须拥有调用该方法的权限。如果程序调用了private方法,就需要设置setAccessible(boolean flag),设置flag为true则取消访问权限检查;false继续执行检查,则会报错Class reflect can not access a member of class MethodClass with modifiers "private"。
设置Class对象变量值 Field.set()/Field.get()
设置/获取任意变量值Object
1 2 3 public native void set (Object obj, Object value) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException;public native Object get (Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException;
Field.setXX()/Field.getXX()
设置/获取基本类型变量int,boolean.long,double,float,char,short,byte8种基本类型
1 2 public native boolean getBoolean (Object obj) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException;public native void setBoolean (Object obj, boolean z) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException;
基本类型
对应名称(位数)
整数型
byte(8位),short(16位),int(32位),long(64位)
浮点型
float(32位),double(64位) 默认为double,要设置成float,需要结尾加f
字节型
char(16位)
布尔型
boolean(1位)
实例分析
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public class reflect {public static void main (String[] args) {try {Object object = methodClass.newInstance();Field field = methodClass.getField("a" );Field declaredField = methodClass.getDeclaredField("b" );true );true );3 );5 );Method addMethod = methodClass.getDeclaredMethod("add" , int .class, int .class);true );1 ,2 );catch (Exception e) {class MethodClass {public int a = 4 ;private int b = 6 ;private int c = 5 ;public MethodClass () {public MethodClass (int a, int b) {this (a, b, 0 );private MethodClass (int a, int b, int c) {this .a = a;this .b = b;this .c = c;private int add (int a, int b) {"reflect value a=" + this .a+" b=" + this .b);return a + b;public int sub (int a, int b) {return a - b;3 b=5
Java反射机制的高级运用 反射创建数组
数组是一个比较特殊的类型,在反射机制中有专门的处理类——java.lang.reflect.Array
newInstance():创建一个数组对象
get()/getXX():获取数组中对应位置的值
set()/setXX():设置数组中对应位置的值
实例分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class GenerateArray {public static void main (String[] args) {try {"java.lang.String" );Object array = Array.newInstance(clazz,20 );0 ,"12" );1 ,"23" );1 ));catch (Exception e){23
反射获取泛型 Java - 泛型
反射只能对普通类型的Field有效,如果该Field的类型是有泛型限制的类型,例如Map<String,String>类型,则无法准备取得该Field的泛型参数。
ParameterizedType代表被参数化的类型,增加了泛型限制的类型。
getRawType()返回没有泛型信息的原始类型
getActualTypeArguments()返回泛型参数的类型
实例分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 public class GenerateArray {private Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap <>();public static void main (String[] args) {try {Field f = clazz.getDeclaredField("map" );Type type = f.getGenericType();if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {ParameterizedType pType = (ParameterizedType) type;Type rType = pType.getRawType();"原始类型 :" + rType);"泛型类型 :" );for (int i = 0 ; i < types.length; i++) {else {"无法获取泛型类型" );catch (Exception e) {
反射使用注意事项 由于反射会额外的消耗一定的系统资源,如果不需要动态的创建一个对象,那么就不需要用到反射。
另外反射调用方法时会忽略权限检查,因此可能会破坏封装性导致安全问题。
只有在 初始化直接赋值且非new(eg: final String aa = "123")不能被反射修改final值。
反射优化 反射慢的原因主要在两点:
虽然javac不怎么优化代码,但反射导致JIT编译器无法有效做优化,使得反射执行慢
反射方法的检测,需要检测类、方法是否存在,权限是否正确
优化点如下:
setAccessible(true)避免反射时的检测若大量执行反射,对反射对象的反射结果进行缓存,可以后续反射时直接调用缓存
使用三方反射库,例如ReflactASM通过添加字节码的方式实现反射功能。
参考链接 Java反射效率低原因