Service工作过程 Service分为两种工作状态,一种是启动状态,主要用于执行后台计算;另一种是绑定状态,主要用于其他组件和Service的交互。
Service的这两种状态是可以共存的,即Service既可以处于启动状态也可以同时处于绑定状态。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 new Intent (this ,MyService.class);new Intent (this ,MyService.class);
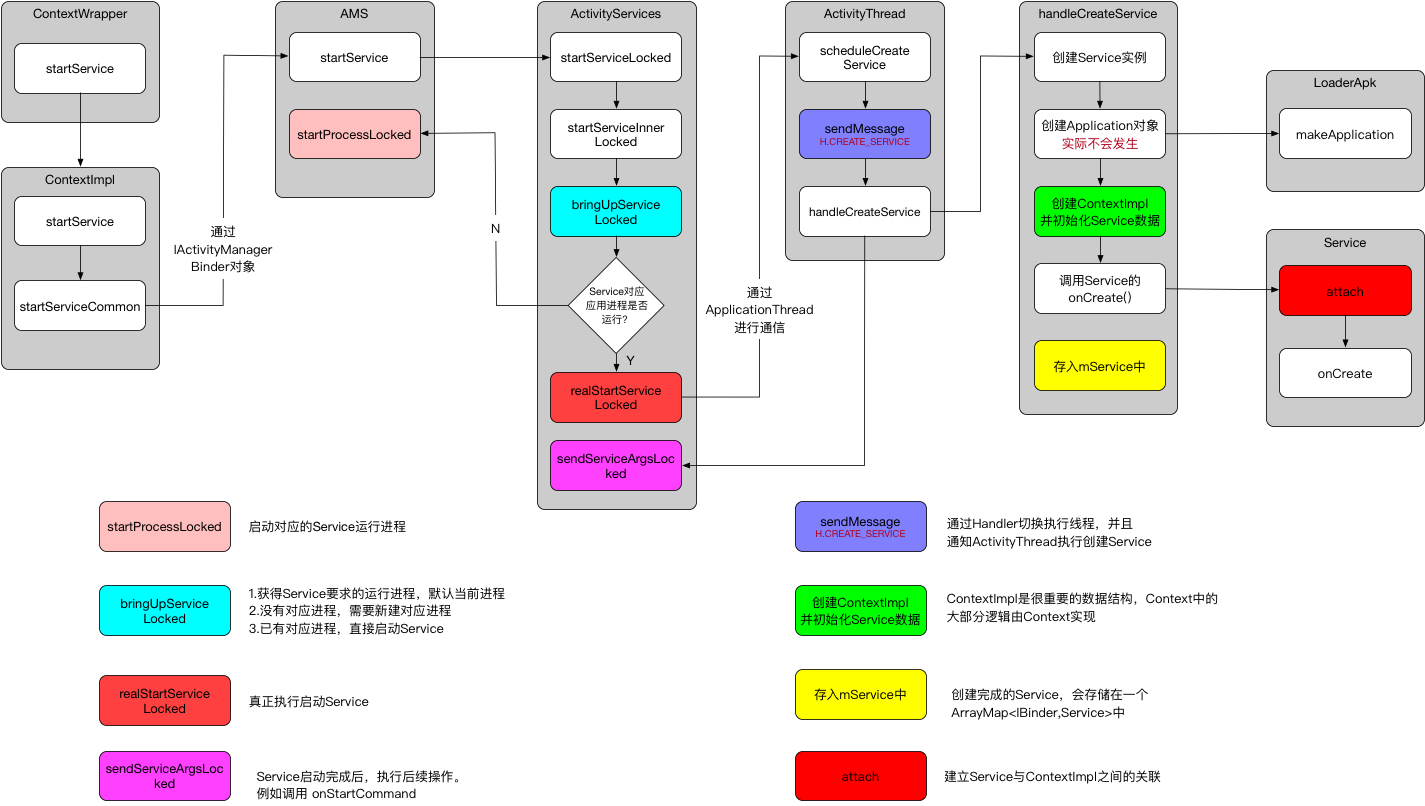
Service启动过程 - startService Service的启动过程从ContextWrapper.startService()开始
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Override public ComponentName startService (Intent service) {return mBase.startService(service);
在Activity启动的时候performLaunActivity时,会创建上下文对象Context,然后在Activity.attach()调用了attachBaseContext()将得到的contenxt进行赋值。最终操作的就是ContextImpl。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Override public ComponentName startService (Intent service) {return startServiceCommon(service, false , mUser);private ComponentName startServiceCommon (Intent service, boolean requireForeground, UserHandle user) {try {this );ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(if (cn != null ) {return cn;catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
ActivityManager.getService()在Activity启动过程中有介绍它是得到IActiivtyManager实际就是指向AMS的一个Binder对象,调用到的就是AMS.startService()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 @Override public ComponentName startService (IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {"startService" );if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("File descriptors passed in Intent" );if (callingPackage == null ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("callingPackage cannot be null" );if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE,"*** startService: " + service + " type=" + resolvedType + " fg=" + requireForeground);synchronized (this ) {final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();try {finally {return res;
mServices的类型是ActiveServices.ActiveServices是一个辅助AMS进行Service管理的类,其中包括Service的启动,绑定和停止等功能。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 startServiceLocked (IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType, int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {ServiceLookupResult res = true , callerFg, false );if (res == null ) {return null ;if (res.record == null ) {return new ComponentName ("!" , res.permission != null "private to package" );ServiceRecord r = res.record;ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
ServiceRecord描述的是一个Service记录,一直贯穿着整个Service的启动过程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked (ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r, boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false , false );if (error != null ) {return new ComponentName ("!!" , error);return r.name;private String bringUpServiceLocked (ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg, boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired) throws TransactionTooLargeException {final String procName = r.processName;String hostingType = "service" ;if (!isolated) {false );if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid" app=" + app);if (app != null && app.thread != null ) {try {return null ;catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {throw e;catch (RemoteException e) {"Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);else {if (WebViewZygote.isMultiprocessEnabled()"webview_service" ;if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true , intentFlags,false , isolated, false )) == null ) {String msg = "Unable to launch app " "/" " for service " ": process is bad" ;return msg;if (isolated) {
在bringUpServiceLocked()中,优先获取Service需要的运行进程--通过android:process设置,然后去判断当前进程中是否存在符合要求的
不存在,调用AMS.startProcessLocked()去新建对应应用进程,这个函数在Activity启动过程中有讲解
存在,直接调用realStartServiceLocked()去启动Service,命名方法类似Activity启动过程中的realStartActivityLocked()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 private final void realStartServiceLocked (ServiceRecord r, ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {boolean created = false ;try {true ;catch (DeadObjectException e) {"Application dead when creating service " + r);throw e;finally {if (!created) {final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);if (newService) {null ;if (!inDestroying) {false );if (r.startRequested && r.callStart && r.pendingStarts.size() == 0 ) {new ServiceRecord .StartItem(r, false , r.makeNextStartId(),null , null , 0 ));true );private final void sendServiceArgsLocked (ServiceRecord r, boolean execInFg, boolean oomAdjusted) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
app.thread是IApplicationThread类型的,实际上是一个Binder对象,它的实现是ApplicationThread,用于和ActivityThread进行通信。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 public final void scheduleCreateService (IBinder token, ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {false );CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData ();
这里与Activity启动过程是一致的,通过ActivityThread.H这个Handler对象发送消息,切换到主线程去处理消息。这个发送的是CREATE_SERVICE,最后调用到了ActivityThread.handleCreateService()去启动Service
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 final ArrayMap<IBinder, Service> mServices = new ArrayMap <>(); private void handleCreateService (CreateServiceData data) {LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(Service service = null ;try {ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();catch (Exception e) {if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {throw new RuntimeException ("Unable to instantiate service " + data.info.name": " + e.toString(), e);try {if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this , packageInfo);Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false , mInstrumentation);this , data.info.name, data.token, app,try {0 , 0 );catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();catch (Exception e) {if (!mInstrumentation.onException(service, e)) {throw new RuntimeException ("Unable to create service " + data.info.name": " + e.toString(), e);
handleCreateService()执行了以下的几件事:
通过类加载器创建Service实例,Actiivty启动过程是利用了 Instrumention.newActivity() 执行相同创建实例
makeApplication()创建Application对象并调用其onCreate创建ContextImpl对象并调用Service.attach()建立关系
最后调用Service.onCreate()开始创建过程,并存储至ArrayMap<IBinder,Service>中,在下一节会介绍这里存储数据的作用
调用onCreate()之后,Service也已经启动了。
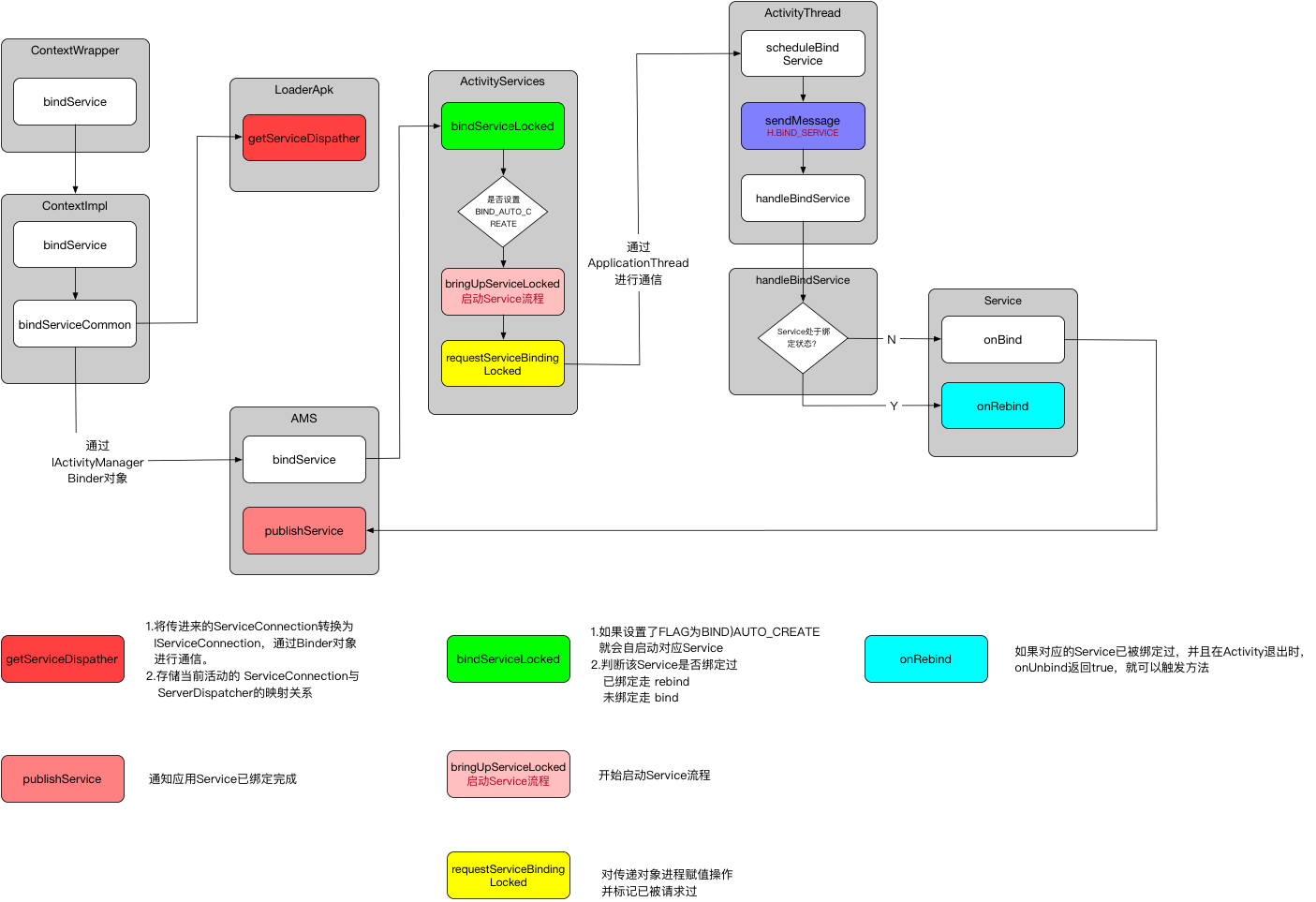
Service绑定过程 - bindService 和Service的启动过程一样,Service的绑定过程也是从ContextWrapper开始
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Override public boolean bindService (Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 @Override public boolean bindService (Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, mMainThread.getHandler(),private boolean bindServiceCommon (Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags, Handler handler, UserHandle user) {if (conn == null ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("connection is null" );if (mPackageInfo != null ) {else {throw new RuntimeException ("Not supported in system context" );try {this );int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindService(if (res < 0 ) {throw new SecurityException ("Not allowed to bind to service " + service);return res != 0 ;catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
在bindServiceCommon()主要做了两件事情:
getServiceDispatcher() 将传进来的ServiceConnection转化成IServiceConnection,通过Binder对象进行通信。使得Service的绑定支持跨进程调用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher (ServiceConnection c, Context context, Handler handler, int flags) {synchronized (mServices) {ServiceDispatcher sd = null ;if (map != null ) {if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Returning existing dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);if (sd == null ) {new ServiceDispatcher (c, context, handler, flags);if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Creating new dispatcher " + sd + " for conn " + c);if (map == null ) {new ArrayMap <>();else {return sd.getIServiceConnection();
mServices存储了一个应用当前活动的ServiceConnection和ServiceDispatcher的映射关系。ServiceDispatcher的作用是连接ServiceConnection和IServiceConnection。
bindService()开始Service的绑定流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public int bindService (IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service, String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {"bindService" );if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("File descriptors passed in Intent" );if (callingPackage == null ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("callingPackage cannot be null" );synchronized (this ) {return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
存储好对应的ServiceConnection和ServiceDispatcher映射的关系,之后开始继续绑定流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 int bindServiceLocked (IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service, String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String callingPackage, final int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);if (callerApp == null ) {throw new SecurityException ("Unable to find app for caller " + caller" (pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid()") when binding service " + service);ActivityRecord activity = null ;if (token != null ) {if (activity == null ) {"Binding with unknown activity: " + token);return 0 ;ServiceRecord s = res.record;if (mAm.mPermissionReviewRequired) {if (mAm.getPackageManagerInternalLocked().isPermissionsReviewRequired(RemoteCallback callback = new RemoteCallback (new RemoteCallback .OnResultListener() {@Override public void onResult (Bundle result) {synchronized (mAm) {final long identity = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();try {if (...) {try {catch (RemoteException e) {else {finally {final Intent intent = new Intent (Intent.ACTION_REVIEW_PERMISSIONS);new Runnable () {@Override public void run () {new UserHandle (userId));try {if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0 ) { if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false ,null ) {return 0 ;if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) { try {false );catch (Exception e) {if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {true );else if (!b.intent.requested) { false );finally {return 1 ;
介绍几个与Service有关的对象类型:
ServiceRecord:描述一个Service
ProcessREcord:描述一个进程的信息
ConnectionRecord:描述应用程序进程和Service建立的一次通信。
AppBindRecord:维护Srvice与应用程序进程之间的关联。
IntentBindRecord:描述绑定Service的Intent
bindServiceLocked()内部会通过bringUpServiceLocked()自动启动Service。然后向下走启动Service流程。
还会多调用一个requestServiceBindingLocked()请求绑定过程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked (ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i, boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {if (r.app == null || r.app.thread == null ) {return false ;if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.d(TAG_SERVICE, "requestBind " + i + ": requested=" + i.requested" rebind=" + rebind);if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0 ) {try {"bind" );if (!rebind) {true ;true ;false ;catch (... ) {return true ;
app.thread把逻辑切换到了 ActivityThread中了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 public final void scheduleBindService (IBinder token, Intent intent, boolean rebind, int processState) {false );BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData ();if (DEBUG_SERVICE)"scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid=" " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());private void handleBindService (BindServiceData data) {Service s = mServices.get(data.token);if (DEBUG_SERVICE)"handleBindService s=" + s + " rebind=" + data.rebind);if (s != null ) {try {try {if (!data.rebind) {IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);else {0 , 0 );catch (RemoteException ex) {throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();catch (Exception e) {if (!mInstrumentation.onException(s, e)) {throw new RuntimeException ("Unable to bind to service " + s" with " + data.intent + ": " + e.toString(), e);
Service.onRebind()执行条件为:使用Service的流程是,先startService()然后bindService(),在Activity退出的时候,Service并不会停止,再进入Activity重新进行bindService(),会触发onRebind()方法。但是先前Activity退出时调用的onUnbind()返回为true,直接写死返回结果。
当多次绑定同一个Service时,onBind()只会执行一次,除非Service被终止。
Service绑定通知 发现Service未绑定时,就会调用到onBind(),Service就处于绑定状态,但是客户端无法感知到Service已经连接成功,所以需要AMS进行通知。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public void publishService (IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("File descriptors passed in Intent" );synchronized (this ) {if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("Invalid service token" );
mServices就是ActiveServices对象,调用其内部的publishServiceLocked()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 void publishServiceLocked (ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();try {for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1 ; conni>=0 ; conni--) {for (int i=0 ; i<clist.size(); i++) {ConnectionRecord c = clist.get(i);try {false );catch (Exception e) {"Failure sending service " + r.name +" to connection " + c.conn.asBinder() +" (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")" , e);false );finally {
c.conn指向IServiceConnection,他是ServiceConnection在本地的代理对象,用于解决当前应用程序进程和Service跨进程通信的问题。
他的具体实现为ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 static final class ServiceDispatcher {private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection .Stub {final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;new WeakReference <LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);public void connected (ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) throws RemoteException {ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();if (sd != null ) {public void connected (ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {if (mActivityThread != null ) {new RunConnection (name, service, 0 , dead));else {
mActivityThread是一个Handler对象,指向的就是ActivityThread.H。因此可以通过调用post()直接发送RunConnection对象的内容运行在主线程中。mActivityThread不可能为空。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 private final class RunConnection implements Runnable {int command, boolean dead) {public void run () {if (mCommand == 0 ) {else if (mCommand == 1 ) {final ComponentName mName;final IBinder mService;final int mCommand;final boolean mDead;
调用了RunConnection实际上还是调用了doConnected()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ServiceConnection mConnection;public void doConnected (ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {synchronized (this ) {if (old != null ) {if (dead) {if (service != null ) {
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection () {@Override public void onServiceConnected (ComponentName name, IBinder service) {@Override public void onServiceDisconnected (ComponentName name) {
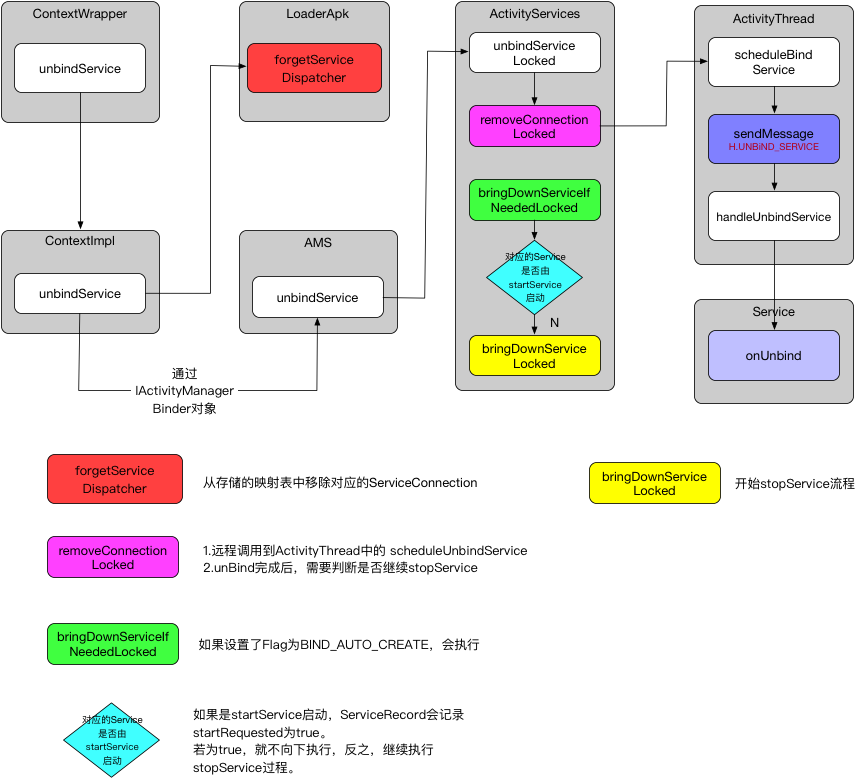
Service解绑过程 - unbindService() Service的解绑过程也是从ContextWrapper开始
1 2 3 4 @Override public void unbindService (ServiceConnection conn) {
实际调用的是ContextImpl.unbindService()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public void unbindService (ServiceConnection conn) {if (conn == null ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("connection is null" );if (mPackageInfo != null ) {IServiceConnection sd = mPackageInfo.forgetServiceDispatcher(try {catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();else {throw new RuntimeException ("Not supported in system context" );
这里主要分为两部分:
调用到ActiveServices.unbindServiceLocked()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 boolean unbindServiceLocked (IServiceConnection connection) {IBinder binder = connection.asBinder();if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "unbindService: conn=" + binder);if (clist == null ) {"Unbind failed: could not find connection for " return false ;final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();try {while (clist.size() > 0 ) {ConnectionRecord r = clist.get(0 );null , null );finally {return true ;void removeConnectionLocked ( ConnectionRecord c, ProcessRecord skipApp, ActivityRecord skipAct) {IBinder binder = c.conn.asBinder();AppBindRecord b = c.binding;ServiceRecord s = b.service;if (clist != null ) {if (clist.size() == 0 ) {if (!c.serviceDead) {if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Disconnecting binding " + b.intent": shouldUnbind=" + b.intent.hasBound);if (s.app != null && s.app.thread != null && b.intent.apps.size() == 0 try {false , "unbind" );if (b.client != s.app && (c.flags&Context.BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY) == 0 false , null );true );false ;false ;catch (Exception e) {"Exception when unbinding service " + s.shortName, e);if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0 ) {boolean hasAutoCreate = s.hasAutoCreateConnections();if (!hasAutoCreate) {if (s.tracker != null ) {false , mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(),true , hasAutoCreate);
又看到了熟悉的app.thread就知道切换回到了ActivityThread
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public final void scheduleUnbindService (IBinder token, Intent intent) {BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData ();private void handleUnbindService (BindServiceData data) {Service s = mServices.get(data.token);if (s != null ) {try {boolean doRebind = s.onUnbind(data.intent);try {if (doRebind) {else {0 , 0 );catch (RemoteException ex) {throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();catch (Exception e) {
当Service调用onUnbind()之后,还需要做一件事情,如果是靠bindService()并配置flag为BIND_AUTO_CREATE。那么后续还会执行到stopService()中的流程,即会调用到Service.onDestroy()。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void removeConnectionLocked ( //如果是利用 BIND_AUTO_CREATE的flag就会向下调用 if ((c.flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0 ) {boolean hasAutoCreate = s.hasAutoCreateConnections();if (!hasAutoCreate) {if (s.tracker != null ) {false , mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(),true , hasAutoCreate);
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 private final void bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked (ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn, boolean hasConn) {if (isServiceNeededLocked(r, knowConn, hasConn)) {return ;if (mPendingServices.contains(r)) {return ;private final boolean isServiceNeededLocked (ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn, boolean hasConn) {if (r.startRequested) {return true ;if (!knowConn) {if (hasConn) {return true ;return false ;
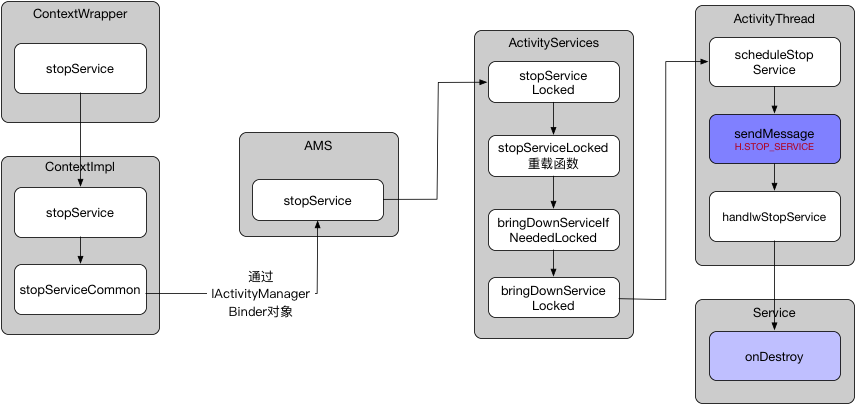
Service停止过程 - stopService() 还是由ContextWrapper.stopService()开始执行
1 2 3 4 @Override public boolean stopService (Intent name) {return mBase.stopService(name);
向下执行到ContextImpl.stopService()中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Override public boolean stopService (Intent service) {return stopServiceCommon(service, mUser);private boolean stopServiceCommon (Intent service, UserHandle user) {try {this );int res = ActivityManager.getService().stopService(if (res < 0 ) {throw new SecurityException ("Not allowed to stop service " + service);return res != 0 ;catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
ActivityManager.getService()实际就是指向ActivityManagerService的一个Binder对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Override public int stopService (IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType, int userId) {"stopService" );if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true ) {throw new IllegalArgumentException ("File descriptors passed in Intent" );synchronized (this ) {return mServices.stopServiceLocked(caller, service, resolvedType, userId);
mServices是ActiveServices的一个实际对象。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 int stopServiceLocked (IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType, int userId) {ServiceLookupResult r = retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, null ,false , false , false );if (r != null ) {if (r.record != null ) {final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();try {finally {return 1 ;return -1 ;return 0 ;private void stopServiceLocked (ServiceRecord service) {false ;if (service.tracker != null ) {false , mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(),false ;false , false );private final boolean isServiceNeededLocked (ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn, boolean hasConn) {if (r.startRequested) {return true ;if (!knowConn) {if (hasConn) {return true ;return false ;private final void bringDownServiceIfNeededLocked (ServiceRecord r, boolean knowConn, boolean hasConn) {if (isServiceNeededLocked(r, knowConn, hasConn)) {return ;if (mPendingServices.contains(r)) {return ;
最后调用到了bringDownServiceLocked()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 private final void bringDownServiceLocked (ServiceRecord r) { if (r.app != null ) {synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {if (r.whitelistManager) {if (r.app.thread != null ) {false );try {false , "destroy" );true ;true );catch (Exception e) {"Exception when destroying service " else {if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v("Removed service that has no process: " + r);else {if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v("Removed service that is not running: " + r);
app.thread切换到ApplicaitonThread继续执行流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public final void scheduleStopService (IBinder token) {private void handleStopService (IBinder token) {Service s = mServices.remove(token);if (s != null ) {try {if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Destroying service " + s);Context context = s.getBaseContext();if (context instanceof ContextImpl) {final String who = s.getClassName();"Service" );try {0 , 0 );catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();catch (Exception e) {else {
最后执行到Service.onDestroy完成停止流程。
拓展 为什么Activity退出时bindService()的Service会一并销毁?
观察源码发现,bindService()也会去启动Service,但为什么没有回调到onStartCommand()?