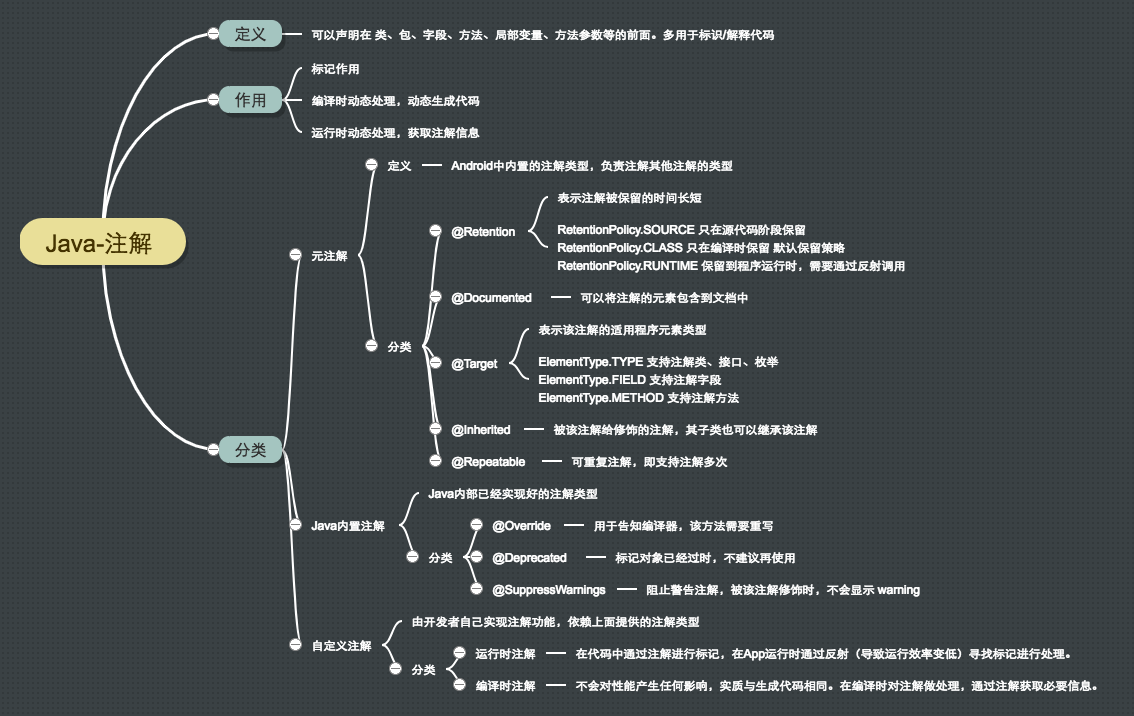
基础概念
元数据
元数据是关于数据的数据,元数据是添加到程序元素入方法、字段、类和包上的额外信息。对数据进行说明描述。
元数据可用于以下场景:
- 编写文档:根据程序元素的注释创建文档
- 代码分析:通过标识的元数据对代码进行分析(例如声明方法重载)
- 编译检查:让编译器实现基本的编译检查,例如*@notNull——不为空*
Java平台的元数据体现 就在于注解(Annotation)。
注解概念
与Java 5之后引入的一个特性,可以声明在类、包、字段、方法、局部变量、方法参数等的前面。多用于标识/解释代码。
注解作用
- 标记作用 @Override 标记重写父类方法
- 编译时动态处理,动态生成代码 @BindView(R.id.view) ButterKnife
- 运行时动态处理,获取注解信息 @Post(“”) Retrofit
注解分类
元注解
Android系统内置的注解类型,负责注解其他注解的注解类型
以下介绍4个常用的元注解
@Retention
保留注解。表示注解被保留的时间长短
1
2
3
4
| @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Annotation_Retention{
}
|
其中RetentionPolicy有三种类型,对应三种保留策略。
| RetentionPolicy(安保留时长排序) |
含义 |
| RetentionPolicy.SOURCE |
注解只在源代码阶段保留,编译器编译时会被忽视 |
| RetentionPolicy.CLASS(默认保留策略) |
注解只保留在编译时编译时注解 |
| RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME |
注解保留到程序运行时,并且会被加载到JVM中,程序运行时可以获取到他们运行时注解 |
@Documented
Java文档注解。可以将注解的元素包含到文档中
1
2
3
4
| @Documented
public @interface Annotation_Documented{
}
|
@Target
表示该注解类型的适用程序元素类型。
1
2
3
4
| @Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Annotation_Target{
}
|
如果未设置@Target类型,默认适用于所有8大元素。
其中ElementType有8种类型,对应8种限制范围。
| ElementType |
含义 |
| ANNOTATION_TYPE |
注解类型声明 |
| CONSTRUCTOR |
构造方法声明 |
| FIELD |
字段声明 |
| LOCAL_VARIABLE |
局部变量声明 |
| METHOD |
方法声明 |
| PACKAGE |
包声明 |
| PARAMETER |
参数声明 |
| TYPE |
类、接口、枚举声明 |
@Inherited
继承注解。如果某个类使用了@Inherited修饰的注解,那么其子类也继承该注解。
1
2
3
4
| @Inherited
public @interface Annotation_Inherited{
}
|
Java 8之后新增的元注解
@Repeatable
可重复注解,被注解的对象可以取多个值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public @interface Job {
Person[] value();
}
@Repeatable(Job.class)
pulic @interface Person {
String role() default "";
}
@Person(role="1")
@Person(role="2")
class Test(){
}
|
Java内置注解
Java内部已经实现好的注解类型
@Override
用于告知编译器,该方法需要被覆写。
1
2
3
4
| @Override
public void onPause(){
}
|
@Deprecated
标记对象已经过时,不建议使用。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class Test{
@Deprecated
public void test(){
}
}
Test test = new Test();
|
最终显示:test.test();
@SuppressWarnings
阻止警告注解,被该注解标记时,不会显示warning
@FunctionalInterface
Java8后引入,标记该对象可以实现函数式接口。
1
2
3
4
| @FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
|
自定义注解
由开发者自己实现注解功能,依赖上面系统提供的注解类型
运行时注解
在代码中通过注解进行标记,在运行时通过反射寻找标价进行处理。由于反射导致运行低效。
定义注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})
@interface CustomAnnotation {
String value() default "";
}
|
注解解析
主要要使用到以下的方法:
| 方法 |
含义 |
| T getAnnotation(Class annotationClass) |
存在annotationClass对应的注解时,返回对应的注解对象 |
| Annotation[] getAnnotations() |
返回该元素上的所有注解,包括继承于基类的注解 |
| Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() |
返回自身显式标明的所有注解 |
| boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) |
存在annotationClass对应的注解时,返回true |
不同位置的注解需要使用不同的解析方式,主要分为3种:
获取类的注解信息
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
| @CustomAnnotation(value = "AnnotationClass")
public class Test{
}
|
解析代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public static void getAnnotationClass(Class clazz) {
boolean hasAnnotation = clazz.isAnnotationPresent(CustomAnnotation.class);
if (hasAnnotation) {
CustomAnnotation contentView = clazz.getAnnotation(CustomAnnotation.class);
System.err.println("Class " + contentView.value());
}
}
|
获取方法的注解信息
示例代码:
1
2
3
4
| @CustomAnnotation(value = "AnnotationMethod")
private void method() {
}
|
解析代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| private static void getAnnotationMethod(Class clazz, String methodName) {
try {
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName);
if (method != null) {
method.setAccessible(true);
Annotation[] ans = method.getDeclaredAnnotations();
for (int i = 0; i < ans.length; i++) {
if (ans[i].annotationType() == CustomAnnotation.class) {
CustomAnnotation contentView = method.getAnnotation(CustomAnnotation.class);
System.err.println("Method " + contentView.value());
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
获取变量的注解信息
示例代码:
1
2
| @CustomAnnotation(value = "AnnotationVar")
int annotationVar = 0;
|
解析代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private static void getAnnotationVar(Class clazz, String varName) {
try {
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(varName);
field.setAccessible(true);
CustomAnnotation contentView = field.getAnnotation(CustomAnnotation.class);
if (contentView != null) {
System.err.println("Field " + contentView.value());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
编译时注解
不会对性能产生任何影响,实质就是生成代码,在编译时对注解做处理,通过注解获取必要信息,在项目中生成代码,于运行时调用。
定义注解
1
2
3
4
5
6
| @Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface MyAnnotation{
int value() default 0;
}
|
注解解析
关键点在于注解的解析器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @SupportedAnnotationTypes("com.wxy.route.test.MyAnnotation")
public class MyAnnotationProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) {
}
}
|
内容引用
注解生成Java代码
